Using the Past Perfect Tense

Are you wondering when to use the past perfect tense? We will go over several different ways this tense is used with plenty of examples to help make everything clear.
[Note: Click here to learn how to form the past perfect.]
Past perfect tense use #1: Completed action before another past action
We use the past perfect to talk about past actions that happened before another past action or situation in the past.
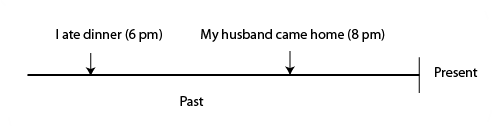
For example: I had eaten dinner before my husband came home.
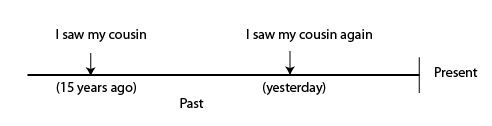
I had not seen my cousin in 15 years.
More examples:
- She hadn’t remembered her key was in the house before she closed the door.
- My boss had already left the office before I finished the report.
- Unfortunately, we hadn’t made a hotel reservation before the trip.
- What had you eaten before you got sick?
- I had eaten some oysters the night before.
Use #2: To explain the reason for something in the past
The past participle can be used to explain why something happened in the past.
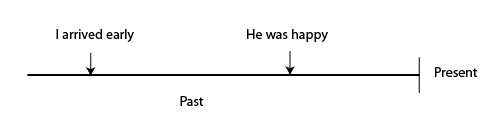
For example: He was happy because I had arrived early.
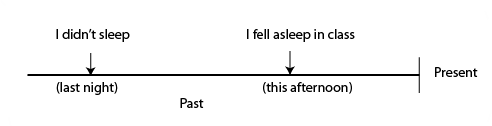
I fell asleep in class because I hadn’t slept the night before.
More examples:
- The pan burned because the water had boiled away.
- We hadn't left early enough so we were late for the party.
- My brother hadn't had a date before so he was super nervous at the dance last night.
- She had wanted a new phone for her birthday because her iPhone was cracked.
- I didn't bring my passport because I hadn't thought it was necessary.
Use #3: The third conditional
The third conditional describes past events/actions that never actually happened. The past perfect is used in this construction.
- If I hadn’t had my umbrella with me, I’d have gotten soaking wet.
- I wish my mother had told me more about her childhood.
- If I’d studied more, my score would have been higher.
- If only you had arrived five minutes earlier.
- He wished he'd decided to bring a coat to the game.
Expressions with “as if” / “as though”
The past participle is frequently used with the expressions “as if” and “as though” to indicate something that might have happened in the past but there is uncertainty about whether it happened or not.
- My son acted as if he had finished his homework but he hadn’t.
- My professor looked as though he hadn’t showered in a week.
- It seemed as if the dog had been abused in the past.
- It appeared as if the thief had entered the back door.
- It looked as though the winter had finally ended.
Past perfect and past simple tenses with "before"/"after"
We often use the past simple instead of the past perfect when “before” or “after” are used to describe past events. That is because using either of these words clearly shows that one past event happened before another.
Note: Native speakers typically prefer to use the past simple with before/after.
- I ate dinner before my husband came home. (simple past)
- I'd eaten dinner before my husband came home. (past perfect)
- We saw a movie after we finished dinner. (simple past)
- We saw a movie after we had finished dinner. (past perfect)
If you need to review how to form the past perfect tense please check this page. I go over the positive and negative forms, questions, review the irregular past participles and spelling changes and give lots of examples.
- Home Page ›
- Main Grammar Page ›
- Form: Past Perfect >
- Use: Past Perfect
